C语言实现LSTM算法
1.算法介绍
LSTM,长短期记忆网络,全称为Long Short Term Memory networks。它是基于RNN的一种时间循环神经网络。
在理解LSTM之前,首先需要了解循环神经网络(RNN)的原理。
1.1 RNN与LSTM
人的思维是连续的,思考问题并不会从头开始,而是会“结合上下文”。传统的神经网络并不能做到这点,而RNN正是这一问题的解决方案。
循环神经网络(RNN)中的神经元,可以把输出值作为下一个神经元的输入值的一部分,进而保证神经网络能够连续“思考”。

然而RNN并不完美,它存在“长依赖”的问题。比方说,假设想让RNN根据一段不完整的句子来预测缺失的单词,例如“I grew up in France… I speak fluent ________.”(缺失的单词为French),则有用的信息主要集中在前半句。然而要预测的单词却和前面有用的信息距离较远,这会导致RNN很难学习到有用的信息。
而LSTM解决了RNN的长依赖问题。如图所示,LSTM也是链状结构,但它和RNN的不同之处在于中间的神经元变成了一个较为复杂的细胞,其主要由遗忘门、输入门、输出门和记忆部分组成。而这个模块正是LSTM的核心。

2.算法实现步骤
2.1 读取csv
该步骤代码与前面代码一致,不再重复给出。
2.2 划分数据为k折
该步骤代码与前面代码一致,不再重复给出。
2.3 核心算法
2.3.1 初始化
首先我们需要确定LSTM的细胞数、输入结点数($x_t$的维度)和隐藏结点数($h_t$的维度)。以本节为例,设置输入结点数为2,隐藏结点数为12,细胞数为8。代码如下:
1 | |
依照定义,我们可以初始化LSTM网络的权重矩阵:
1 | |
将权重矩阵的值打印出来结果如下:
1 | |
之后,在训练过程中,我们需要定义二维数组来保存各个门和记忆的数组:
1 | |
2.3.2 构建细胞
LSTM的细胞主要由以下四个部分组成:
- 遗忘门
- 输入门
- 输出门
- 记忆部分
2.3.2.1 遗忘门
遗忘门主要负责接受并筛选上一个细胞的信息。设为遗忘门输出值,为细胞输出值,为输入值,表示激活函数,和代表遗忘门的权重和偏差,其计算公式为:
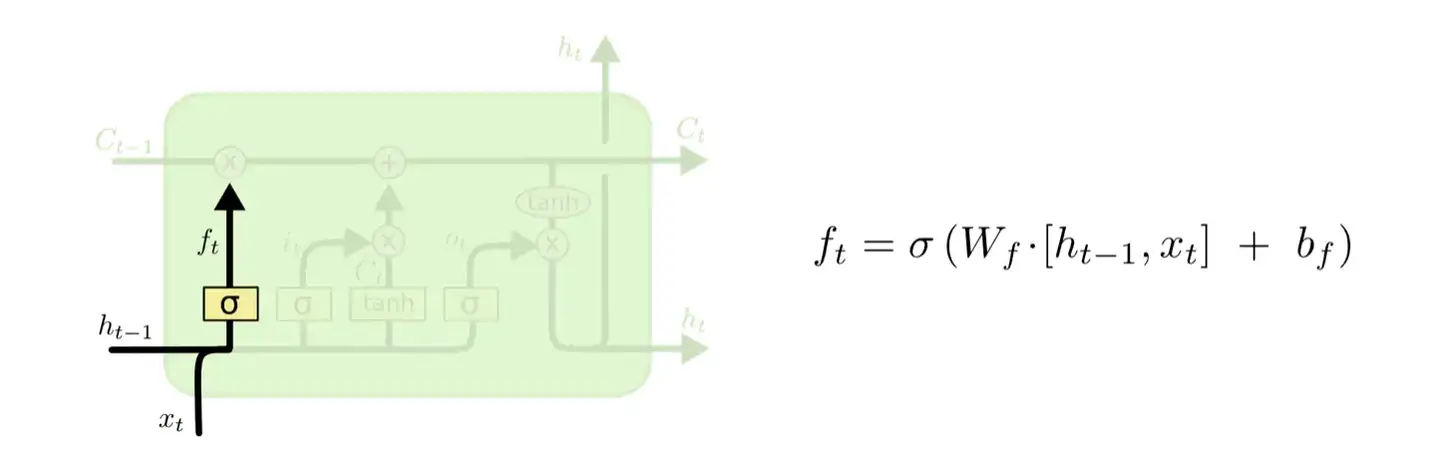
2.3.2.2 输入门
输入门主要负责控制新信息的传入,并将新信息传入记忆中。设和为输入门输出值,、和、代表输入门的权重和偏差,其计算公式为:
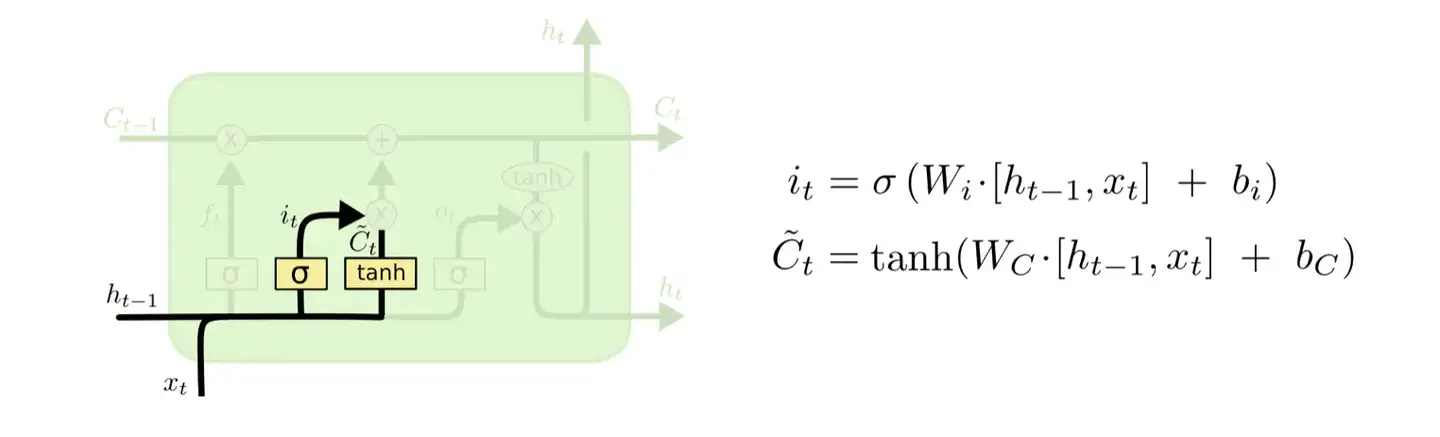
2.3.2.3 记忆部分
记忆主要负责记录该细胞里的信息,并影响后续的细胞。设为记忆值,则公式如下:
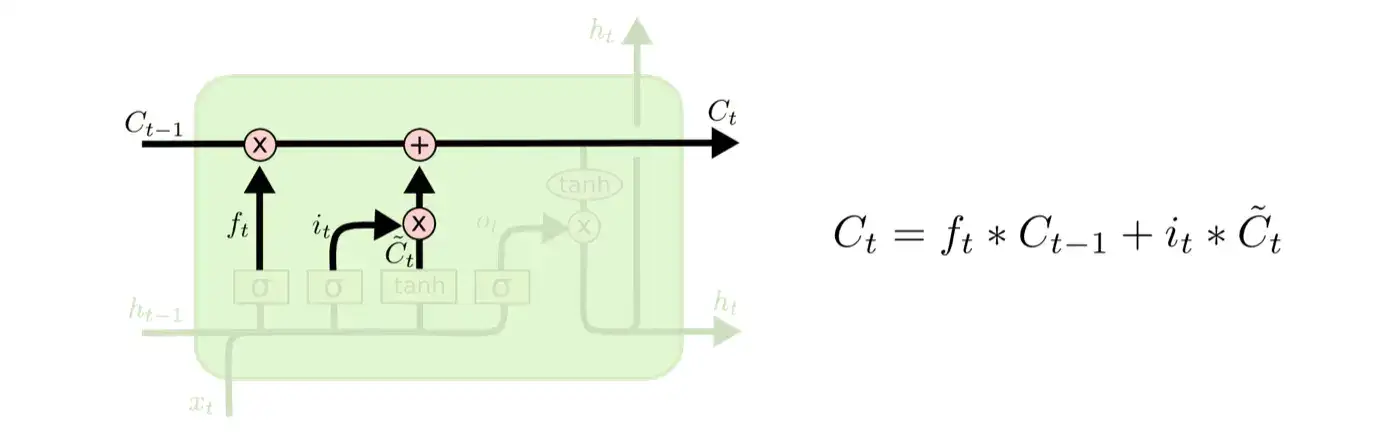
2.3.2.4 输出门
输出门主要负责输出值,同时输出值也将作为下一个细胞输入的一部分。设为细胞输出值,和代表输出门的权重和偏差,则公式如下:
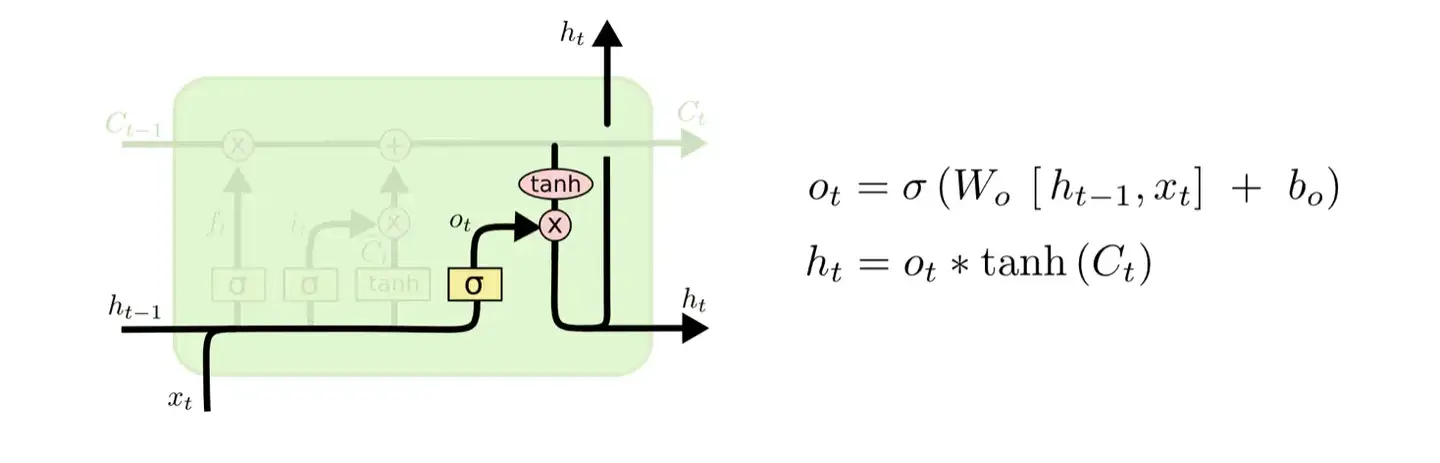
2.3.2.5 代码
将以上四个部分结合起来,便可以构成LSTM的细胞。以本文为例,将LSTM前向传播过程写成代码片段如下:
1 | |
输出的结果如下:
1 | |
2.3.3 反向传播
首先,我们先求预测值和实际值的误差:
1 | |
得到误差如下:
1 | |
之后进行反向传播,更新权值矩阵:
1 | |
结合上述代码,把全新的权重矩阵打印如下:
1 | |
2.3.4 预测
训练完成后,就可以利用训练好的权重矩阵进行预测。其过程和前向传播大致相同。代码如下:
1 | |
2.4 计算RMSE
该步骤代码与前面代码一致,不再重复给出。
2.5 按划分的k折交叉验证计算预测所得平均RMSE
1 | |
3.完整算法及应用
本节将用LSTM网络让模型学习加法,其过程如下:
- 读取数据
- 把数据转换为二进制格式(输入与实际值)
- 训练模型
- 预测
下面给出完整的主函数以及训练函数代码:
main.c:
1 | |
test_prediction.c:
1 | |
最终输出结果如下:
1 | |
B站视频链接:C语言实现机器学习系列教程_哔哩哔哩 (゜-゜)つロ 干杯~-bilibili P22
